- Home
- About Us
- Products
- Chain
- Sprocket
- Pulley & Sheave
- Gearbox\Reducer
- Belt
- Coupling
- Gear Operator &Valve
- Gear\Rack
- Mechanical seal
- Hub & Bushing
- Hydraulic & Pheumatic
- Shaft Collar
- Locking Assembly
- PTO Shaft
- Mechanical parts
- Conveyor component
- universal joints
- Shaft & York
- vibrator, vibration motor
- Starter & Alternator
- Ungrouped
- Other
- Air Compressor
- News
- Download
- Send Inquiry
- Contact Us
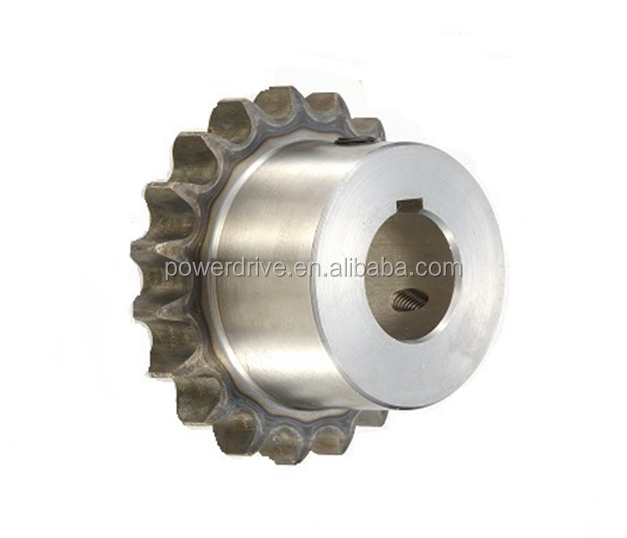
What are the standard specifications for metric sprockets?
If you're sourcing components, you're likely asking, "What are the standard specifications for metric sprockets?" Getting this right is critical. The wrong sprocket can derail production, cause unexpected downtime, and blow your budget. Standard specs like pitch, bore size, and tooth count aren't just numbers on a datasheet; they are the blueprint for your machinery's reliability. Understanding these ensures compatibility with your chain and smooth power transmission. Many procurement specialists face the frustration of mismatched parts or unclear standards. This guide cuts through the complexity, providing a clear, actionable roadmap. We'll break down each key specification, show you what to look for, and highlight how partnering with a specialist like Raydafon Technology Group Co., Limited, with its precise manufacturing and comprehensive catalog, can eliminate these sourcing headaches and deliver lasting performance.
Article Outline:
- Understanding Key Specifications: Pitch, Bore, and Tooth Count
- Material and Hardware Choices for Durability
- Ensuring Perfect Compatibility and Avoiding Costly Mistakes
- FAQs on Metric Sprocket Standards
Understanding Key Specifications: Pitch, Bore, and Tooth Count
Imagine this: You've installed a new sprocket, but within days, the chain starts jumping, creating a jarring noise and threatening to damage the entire drive system. The culprit? An incorrect pitch specification. The pitch is the fundamental measurement, defining the distance between the centers of two adjacent roller pins. Common metric pitches include 8mm, 10mm, 12.7mm, and 25.4mm. Using a 12.7mm pitch chain on a sprocket designed for 12mm will fail catastrophically. Next is the bore—the hole in the center for the shaft. A loose bore causes wobble and misalignment, while a too-tight bore makes installation impossible without damaging the sprocket or shaft. Finally, the tooth count directly affects the speed ratio and torque. More teeth provide smoother operation and higher torque at lower speeds, while fewer teeth are used for higher speed reductions.
The solution is meticulous specification checking. Always cross-reference the chain's pitch with the sprocket's stated pitch. For the bore, know your shaft's exact diameter and any required keyway dimensions. Don't guess; measure. This is where a supplier's expertise is invaluable. Raydafon Technology Group Co., Limited provides detailed technical drawings for every sprocket, listing all critical dimensions to guarantee a perfect fit. Their product data removes ambiguity, ensuring you order the correct component the first time.

| Specification | Description | Common Metric Values |
|---|---|---|
| Pitch (P) | Distance between chain roller centers. | 8B (12.7mm), 10B (15.875mm), 12B (19.05mm) |
| Bore Diameter (d1) | Inner diameter of the sprocket hub. | Customizable from 10mm to 100mm+ |
| Number of Teeth (Z) | Total teeth on the sprocket. | Range from 9T to 120T+ |
| Plate Thickness (b1) | Thickness of the sprocket's side plate. | Varies with size (e.g., 3mm to 15mm) |
Material and Hardware Choices for Durability
Your conveyor system in a wet, dusty warehouse is constantly under stress. A standard carbon steel sprocket begins to rust within months, teeth wear down, and soon you're facing unplanned maintenance and replacement. The problem is material fatigue and corrosion. Standard carbon steel (SS, C45) works for general use but fails in harsh environments. Similarly, using the wrong type of hub (plain, finished bore, or with keyway) or improper mounting hardware leads to slippage and premature failure.
The solution lies in selecting the right material and construction for the operating environment. For high corrosion resistance, stainless steel (SUS304, SUS316) is essential. For extreme wear resistance without lubrication, sintered steel or engineered plastics may be optimal. The hub design must be chosen based on the shaft connection: a finished bore with a keyway and set screws offers the most secure fixation. Raydafon Technology Group Co., Limited excels here, offering a wide range of materials and hub types. They don't just sell parts; they provide engineering solutions. By specifying your environment (wet, dry, high-load, abrasive), they can recommend the ideal sprocket material from their portfolio, significantly extending service life and reducing total cost of ownership.
| Material / Feature | Best For | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel (C45) | General industrial drives, normal conditions. | Cost-effective, good strength. |
| Stainless Steel (SUS304) | Food, chemical, marine, washdown environments. | Excellent corrosion resistance. |
| Hardened Teeth | High-wear applications, abrasive dust. | Extended wear life, reduced downtime. |
| Taper-Lock Bushings | Easy installation/removal, multiple shaft sizes. | Versatility and secure grip. |
Ensuring Perfect Compatibility and Avoiding Costly Mistakes
The final assembly stage: all components have arrived, but the new sprocket doesn't align with the neighboring gear or guard. Now you face project delays, expedited shipping costs for a replacement, and labor waste. This compatibility nightmare stems from overlooking overall dimensions like hub diameter, overall width, and hole pattern. A sprocket might have the correct pitch and bore but be physically too large for the allotted space.
The solution is a holistic review of all dimensional parameters before ordering. Beyond pitch and bore, you must check the hub diameter (D), overall width (B), and the Pitch Diameter (PD) which is critical for center distance calculations between shafts. Utilizing supplier-provided CAD models or detailed dimension tables is crucial. Raydafon Technology Group Co., Limited supports procurement teams by providing complete technical data packages, including 2D drawings and 3D models for easy integration into your system designs. This level of detail ensures mechanical compatibility, prevents installation issues, and streamlines the entire procurement-to-installation workflow, safeguarding your project timeline and budget.
| Compatibility Check | Parameter to Verify | Consequence of Mismatch |
|---|---|---|
| Chain Pairing | Sprocket Pitch vs. Chain Pitch | Chain jump, rapid wear, drive failure. |
| Shaft Fit | Bore Size & Keyway vs. Shaft | Slippage, wobble, damage to shaft/sprocket. |
| Space Constraints | Overall Width (B) & Hub Diameter (D) | Physical interference, inability to install. |
| Drive Design | Pitch Diameter (PD) for Center Distance | Incorrect speed ratio, tension issues. |
FAQs on Metric Sprocket Standards
Q: What are the most critical standard specifications to check when ordering a metric sprocket?
A: The three most critical specifications are: 1) Pitch: Must exactly match your drive chain's pitch (e.g., 08B for 12.7mm). 2) Bore Size & Type: Must match your shaft diameter and connection method (plain bore, keyway, finished bore). 3) Number of Teeth: Determines your speed ratio. Always request a detailed drawing from your supplier, like those provided by Raydafon Technology Group Co., Limited, to confirm all dimensions.
Q: How do I choose between different material grades for a sprocket?
A: Material choice depends on the operating environment. Use carbon steel (e.g., C45) for standard, dry industrial applications. Opt for stainless steel (SUS304/316) for corrosive environments (food processing, chemicals, outdoors). For high-wear situations with abrasives, hardened teeth or sintered steel offer superior life. Consulting with an expert supplier ensures you get a cost-effective solution built to last in your specific conditions.
Selecting the correct metric sprocket is a precise engineering task that directly impacts your operational efficiency and maintenance costs. By focusing on the standard specifications outlined above—pitch, bore, tooth count, material, and overall dimensions—you can make informed, confident purchasing decisions.
For procurement professionals seeking reliability and precision, partnering with an experienced manufacturer is key. Raydafon Technology Group Co., Limited specializes in the manufacture and global supply of high-precision power transmission components, including a comprehensive range of metric sprockets built to exacting standards. With a commitment to quality documentation, technical support, and customized solutions, Raydafon helps you solve compatibility challenges and secure the optimal component for your application. Visit https://www.raydafonmachinery.com to explore their product catalog and technical resources. For specific inquiries and quotes, please contact their sales team at [email protected].
K. L. Johnson, 1972, "The mechanics of the sprocket-chain drive", Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, Vol. 14, No. 4.
H. A. Rothbart, 1996, "Mechanical Design and Systems Handbook", McGraw-Hill, 2nd Edition.
M. F. Spotts, 2004, "Design of Machine Elements", Prentice Hall, 8th Edition.
R. G. Budynas, J. K. Nisbett, 2015, "Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design", McGraw-Hill, 10th Edition.
T. H. C. Childs, 2014, "Mechanical Design: Theory and Applications", Butterworth-Heinemann.
D. B. Marghitu, 2001, "Mechanical Engineers' Handbook", Academic Press.
J. E. Shigley, C. R. Mischke, 1989, "Standard Handbook of Machine Design", McGraw-Hill.
G. Niemann, H. Winter, 2005, "Machine Elements: Design and Calculation in Mechanical Engineering", Springer-Verlag.
A. D. Deutschman, W. J. Michels, C. E. Wilson, 1975, "Machine Design: Theory and Practice", Macmillan.
J. J. Uicker, G. R. Pennock, J. E. Shigley, 2017, "Theory of Machines and Mechanisms", Oxford University Press, 5th Edition.
Previous :
-
Related News
- Can Raydafon flexible couplings be used in harsh environments?
- Is the Raydafon 88K pintle chain compatible with standard sprockets?
- How to choose the right PTO speed reducer gearbox for my equipment?
- What is the typical lifespan of a furniture hydraulic cylinder?
- How do I properly install and align an HTD 8M Series timing pulley?
- How do you install and maintain an elastomeric coupling?
Leave me a message
New Products