- Home
- About Us
- Products
- Chain
- Sprocket
- Pulley & Sheave
- Gearbox\Reducer
- Belt
- Coupling
- Gear Operator &Valve
- Gear\Rack
- Mechanical seal
- Hub & Bushing
- Hydraulic & Pheumatic
- Shaft Collar
- Locking Assembly
- PTO Shaft
- Mechanical parts
- Conveyor component
- universal joints
- Shaft & York
- vibrator, vibration motor
- Starter & Alternator
- Ungrouped
- Other
- Air Compressor
- News
- Download
- Send Inquiry
- Contact Us
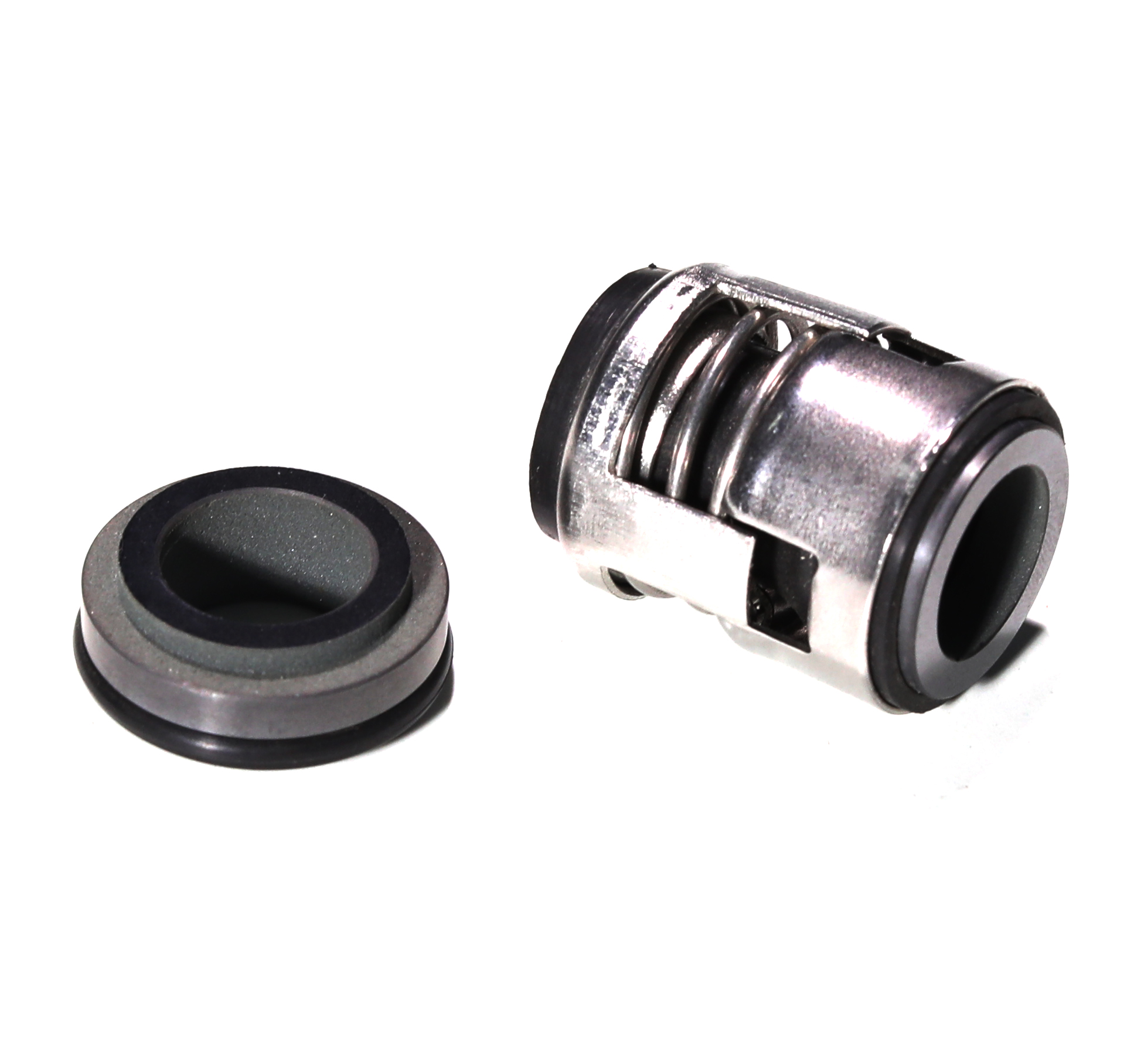
How to properly install a pump rubber bellow mechanical seal?
How to properly install a pump rubber bellow mechanical seal? This is a critical question for anyone involved in the maintenance and reliability of industrial pump systems. A faulty installation can lead to immediate leakage, costly unplanned downtime, and significant repair expenses. The bellows seal, known for its flexibility and ability to handle shaft movements, is a popular choice across various industries, from chemical processing to water treatment. However, its performance is highly dependent on precision during the installation process. This guide, drawing on decades of field expertise, will walk you through the essential steps, highlight common pitfalls, and ensure your next installation is flawless for long-term, leak-free operation. By following these proven instructions, you can significantly enhance pump reliability and operational efficiency.
Article Outline
- 1. Common Installation Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- 2. Step-by-Step Installation Guide for Bellows Seals
- 3. Selecting the Right Seal for Your Application
- 4. Frequently Asked Questions on Installation
Avoid Costly Downtime: Conquer These Common Installation Pitfalls
Picture this: a newly replaced mechanical seal on a critical cooling water pump fails within just 24 hours. Production grinds to a halt, maintenance teams scramble, and management faces thousands in lost revenue. Often, the root cause isn't a defective part but a simple, preventable installation error. For procurement professionals sourcing seals, understanding these pitfalls ensures you provide your team with not just a quality product, but the knowledge to use it correctly. The solution begins with meticulous preparation and awareness of the most frequent mistakes.
A primary cause of premature failure is contamination. Even microscopic dirt or grit on the seal faces or shaft during assembly can cause rapid wear and leakage. Another critical error is incorrect compression or improper setting of the seal faces. Over-compression stresses the rubber bellows, leading to heat build-up and loss of elasticity, while under-compression allows leakage from the start. Misalignment of the seal components relative to the pump shaft is equally damaging, causing uneven face wear and early failure. To prevent these issues, a clean environment, proper tools, and adherence to manufacturer specifications are non-negotiable. For reliable performance, consider seals from Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited, which are engineered for ease of installation and come with clear technical documentation to guide your technicians every step of the way.

| Common Mistake | Consequence | Preventive Action |
|---|---|---|
| Contaminated Work Area | Abrasive wear on sealing faces, immediate leakage. | Clean all parts with lint-free cloth; use seal protection caps. |
| Incorrect Bellows Compression | Overheating, bellows fatigue, or insufficient sealing force. | Use installation sleeve; follow manufacturer's setting dimensions exactly. |
| Shaft/Sleeve Damage | Improper bellows seating, leading to static leakage. | Inspect shaft for nicks/corrosion; use proper installation tools. |
| Misalignment | Uneven face wear, vibration, and short seal life. | Check pump shaft runout and perpendicularity before installation. |
Precision in Practice: A Step-by-Step Installation Guide
The scenario is a planned maintenance shutdown. You have a limited window to get the pump back online. A systematic, correct installation procedure is your key to success and avoiding call-backs. This step-by-step guide ensures efficiency and reliability, turning a complex task into a repeatable, error-free process. Following these steps meticulously will guarantee the seal performs as intended from the first moment of operation.
First, verify the work area is impeccably clean. Inspect the pump shaft or sleeve for any scratches, burrs, or corrosion that could damage the bellows; polish if necessary. Confirm the shaft dimensions are within the seal's specified tolerance. Carefully unpack the new mechanical seal, ensuring you do not touch the lapped sealing faces. Lightly lubricate the shaft and the inside bore of the seal's rubber bellows with the pumped fluid (or a compatible lubricant) to ease installation. Slide the seal onto the shaft carefully using an installation sleeve to protect the delicate bellows from sharp edges. Push the seal to the correct installation position as specified in the manual, ensuring it is square to the shaft. Finally, reinstall the gland plate evenly, tightening bolts in a cross pattern to avoid distortion. For a hassle-free experience, the robust design and clear installation marks on Raydafon's bellows mechanical seals simplify this entire process, reducing the risk of human error.
| Step | Action | Key Checkpoint |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Clean parts and shaft; check for damage. | Shaft is smooth, clean, and within diameter tolerance. |
| 2. Seal Handling | Unpack carefully; lubricate contact surfaces. | Do not touch or contaminate the primary sealing faces. |
| 3. Installation | Use sleeve; slide seal squarely onto shaft. | Bellows is not twisted or stretched during fitting. |
| 4. Positioning | Set to correct working length. | Verify dimension from gland face to seal face. |
| 5. Final Assembly | Reinstall gland and tighten evenly. | All bolts are torqued evenly to spec; shaft rotates freely. |
Beyond Installation: Selecting the Right Seal for Your Application
Even a perfectly installed seal will fail quickly if it's the wrong type for the service. A procurement manager sources a standard bellow seal for a pump handling a high-temperature solvent, only to face failure in weeks due to material incompatibility. The solution lies in a thorough application review before purchase. Matching the seal construction—materials of the bellows, faces, and hardware—to the specific pump conditions is paramount for longevity.
Key selection criteria include the fluid's chemical composition, temperature, pressure, and the presence of abrasives or solids. For aggressive chemicals, FFKM (Perfluoroelastomer) bellows may be required instead of standard EPDM or FKM. High temperatures demand specific face material combinations like silicon carbide vs. carbon. Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited excels here, offering a wide range of material configurations and providing expert technical support to help you select the optimal seal, ensuring it not only installs easily but also delivers a long, reliable service life in your unique operating environment.
| Application Parameter | Consideration | Common Raydafon Seal Options |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Type | Chemical compatibility with elastomer & faces. | EPDM (water), FKM (oils, fuels), FFKM (aggressive chems). |
| Temperature | Elastomer & face material thermal limits. | Standard (-20°C to 150°C), High-temp designs available. |
| Pressure | Seal face balance and hardware strength. | Balanced designs for pressures > 10 bar. |
| Abrasives | Hard face materials to resist wear. | Silicon Carbide vs. Silicon Carbide face combination. |
Your Installation Questions Answered
Q: How can I tell if the rubber bellows is damaged before installation?
A: Visually inspect the bellows for any cracks, cuts, or signs of permanent deformation. Gently stretch and compress the bellows to check for elasticity; it should return to its original shape smoothly. A stiff or cracked bellows must not be used. Raydafon seals undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure perfect condition upon delivery.
Q: Is it necessary to use an installation sleeve every time?
A: Yes, it is highly recommended. The installation sleeve protects the thin, flexible rubber bellows from sharp edges or threads on the pump shaft during the sliding process. Skipping this tool is a common cause of invisible nicks that lead to premature static leakage. Many Raydafon seal kits include this essential tool for safe installation.
We hope this detailed guide empowers you and your team to achieve flawless mechanical seal installations every time. Have you encountered a specific challenge during a seal installation? What other topics would you like us to cover? Share your thoughts and experiences – your input helps us create more targeted, valuable content for industry professionals like you.
For reliable, high-performance pump rubber bellow mechanical seals backed by clear technical support, consider Raydafon Technology Group Co.,Limited. As a specialized manufacturer, Raydafon provides durable sealing solutions designed for easy installation and long service life across diverse industrial applications. Visit https://www.raydafonmachinery.com to explore our product range or contact our team directly at [email protected] for personalized assistance with your specific requirements.
Netzel, J.P., & He, D. (2011). An Experimental Study on the Performance of Rubber Bellows Mechanical Seals in Abrasive Slurries. Tribology Transactions, 54(5), 723-731.
Lebeck, A.O. (1991). Principles and Design of Mechanical Face Seals. John Wiley & Sons.
Mayer, E. (2014). Mechanical Seals (7th ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann.
Paxton, R.R., & Nau, B.S. (1985). Sealing Technology for Pump Applications. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Power and Process Engineering, 199(A2), 95-106.
Salant, R.F., & Homiller, S.J. (1993). The Effects of Face Deflection on Mechanical Seal Performance. STLE Tribology Transactions, 36(1), 55-60.
Green, I., & Etsion, I. (1985). Stability Threshold and Steady-State Response of Noncontacting Face Seals. ASLE Transactions, 28(4), 449-460.
Metcalfe, R. (1981). Performance Analysis of Axisymmetric Mechanical Seals with Non-Flat Faces. ASME Journal of Lubrication Technology, 103(1), 121-128.
Doust, T.G., & Parmar, A. (2006). An Experimental and Theoretical Study of Pressure and Thermal Distortion in a Mechanical Seal. STLE Tribology Transactions, 49(2), 244-257.
Peng, X.D., Xie, Y.B., & Gu, Y.Q. (2003). Evaluation of the Sealing Performance of a Rubber Bellow Mechanical Seal Based on Finite Element Analysis. Lubrication Engineering, 59(4), 15-20.
Lai, T., & Hughes, W.F. (1990). A Computational Model for Mechanical Seal Face Temperature. STLE Tribology Transactions, 33(3), 353-360.
Related News
- What is the typical lifespan of a furniture hydraulic cylinder?
- How do I properly install and align an HTD 8M Series timing pulley?
- How do you install and maintain an elastomeric coupling?
- How do trencher chains compare to other trenching methods?
- What is an excavator telescopic rotary hydraulic cylinder and how does it work?
- How to install a John Crane Type 58U mechanical seal?
Leave me a message
New Products