- Home
- About Us
- Products
- Chain
- Sprocket
- Pulley & Sheave
- Gearbox\Reducer
- Belt
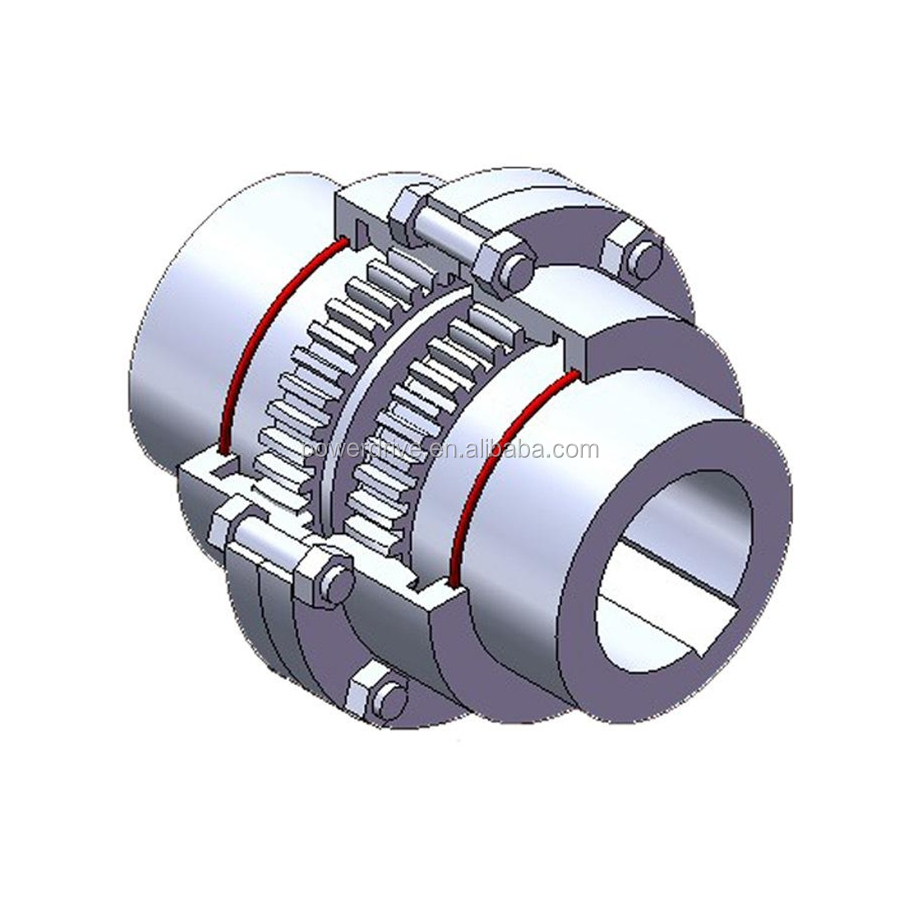
- Coupling
- Gear Operator &Valve
- Gear\Rack
- Mechanical seal
- Hub & Bushing
- Hydraulic & Pheumatic
- Shaft Collar
- Locking Assembly
- PTO Shaft
- Mechanical parts
- Conveyor component
- universal joints
- Shaft & York
- vibrator, vibration motor
- Starter & Alternator
- Ungrouped
- Other
- Air Compressor
- News
- Download
- Send Inquiry
- Contact Us